In recent years, green bonds have gained significant traction in financial markets, reflecting a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility. These financial instruments not only provide investors with an opportunity to contribute to projects that benefit the environment but also represent a shift in market dynamics as businesses and governments increasingly recognize the importance of addressing climate change.
Understanding Green Bonds
What Are Green Bonds?
Green bonds are fixed-income securities specifically designed to raise funds for projects that have positive environmental benefits. The proceeds from green bonds are typically allocated to renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable waste management, clean transportation, and other environmentally friendly projects. The main goal of green bonds is to finance initiatives that contribute to mitigating climate change and promoting sustainability.
Distinguishing Features of Green Bonds
Use of Proceeds: One of the defining characteristics of green bonds is that the proceeds must be used exclusively for projects that promote environmental sustainability. This transparency ensures that investors know their funds are supporting worthy initiatives.
Certification and Standards: Many green bonds undergo rigorous evaluation against established standards. Various organizations, such as the Climate Bonds Initiative and the Green Bond Principles, provide frameworks for issuing green bonds, ensuring accountability and credibility in the market.
Tax Incentives: In some jurisdictions, green bonds may come with tax incentives, enhancing their attractiveness to investors. These incentives can take the form of tax exemptions on interest income, further encouraging investment in sustainable projects.
The Growth of Green Bonds
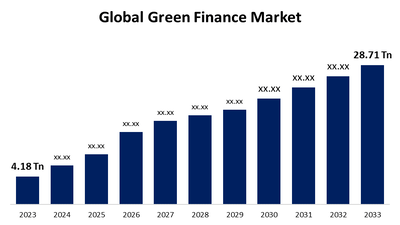
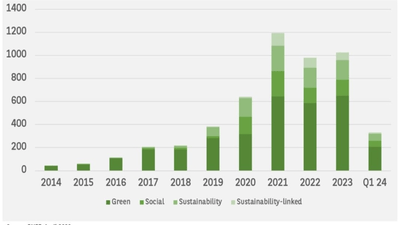
The green bond market has experienced substantial growth since its inception. The first green bond was issued by the European Investment Bank in 2007, marking the beginning of a new era in sustainable finance. Since then, the market has expanded rapidly, fueled by rising investor demand for environmentally responsible investment options.
According to the Climate Bonds Initiative, the global green bond market surpassed ** $ 1 trillion** in issuance by 2022, reflecting a marked increase in both the number of issuers and the volume of funds raised. This growth can be attributed to several factors, including heightened awareness of climate change, regulatory support, and evolving investor preferences.
Key Drivers Behind the Rise of Green Bonds

1. Climate Change Advocacy
The urgent need to address climate change has fueled the growth of the green bond market. As the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events increase, governments and businesses are under increasing pressure to invest in sustainable projects that can mitigate environmental impacts. By allocating funds through green bonds, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
2. Investor Demand for Sustainable Investments
There is a growing demand among investors for environmentally responsible investment options. Institutional investors, in particular, are seeking to align their portfolios with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Green bonds provide a viable avenue for investors to support sustainable initiatives while also receiving competitive returns.
3. Regulatory Support and Frameworks
Many governments and regulatory bodies are actively promoting the issuance of green bonds as part of their broader climate action strategies. Initiatives such as the European Union's Green Deal and the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals have paved the way for increased issuance of green bonds. Regulatory frameworks provide guidance for issuers and enhance transparency, building investor confidence.
4. Corporate Sustainability Goals
As companies increasingly prioritize corporate social responsibility (CSR) and sustainability, many are turning to green bonds as a funding mechanism for their environmental projects. By issuing green bonds, companies can raise capital while simultaneously showcasing their commitment to sustainability and enhancing their brand reputation.
Market Trends in Green Bonds
1. Expanding Market Participants
The green bond market is not limited to government or supranational issuers. Corporations, municipalities, and financial institutions are also entering the space, leading to a more diverse array of green bond offerings. This broader participation is attracting a wider range of investors and enhancing liquidity in the market.
2. Innovative Green Financial Products
As the market matures, innovative financial products are emerging within the green bond space. This includes green loans, sustainability-linked bonds, and green equities, which further expand the options available to investors. These innovative products enable issuers to tailor financing solutions to their specific sustainability goals.
3. Geographical Expansion
While the green bond market initially gained prominence in Europe, it is now becoming a global phenomenon. Issuances are increasing in regions such as Asia, the Americas, and Africa, reflecting a collective recognition of the importance of sustainable finance. For instance, China has become a significant player in the green bond market, issuing a considerable volume of green bonds to finance renewable energy projects.
4. Increasing Focus on Impact Measurement
As the green bond market evolves, there is a growing emphasis on measuring the environmental impact of funded projects. Investors and stakeholders are demanding greater transparency and accountability regarding the outcomes achieved through green bond financing. This has led to the development of standardized impact reporting frameworks, allowing issuers to provide data on the environmental benefits of their projects.
The Benefits of Investing in Green Bonds
1. Financial Returns
Green bonds can offer competitive financial returns, making them an attractive investment for those seeking to balance financial performance with social responsibility. Many green bonds carry credit ratings comparable to traditional bonds, providing investors with a level of safety while supporting sustainable initiatives.
2. Portfolio Diversification
Incorporating green bonds into an investment portfolio can enhance diversification. By adding green bonds to a portfolio, investors can reduce risk exposure while tapping into the growing market for sustainable finance.
3. Alignment with Personal Values
Investing in green bonds allows individuals to align their financial decisions with their values and beliefs. As more people become conscious of environmental issues, green bonds offer a means to support projects that foster positive change, contributing to a more sustainable world.
4. Attractive for Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as pension funds and insurance companies, are increasingly seeking green bonds to meet their sustainability objectives. By integrating green bonds into their investment strategies, institutional investors can fulfill their ESG commitments while achieving financial growth.
Challenges Facing the Green Bond Market
1. Ambiguity in Definitions
One of the major challenges facing the green bond market is the lack of standardized definitions for what constitutes a "green" project. Discrepancies in labeling can lead to greenwashing, where issuers exaggerate the environmental benefits of their bonds. This uncertainty can undermine investor confidence and hinder market growth.
2. Limited Awareness and Education
While awareness of green bonds is growing, many investors and issuers remain unsure of how to navigate the market. Increased education and resources are necessary to help stakeholders understand the benefits and risks associated with green bonds.
3. Regulatory Hurdles
In some regions, regulatory frameworks are still developing, which can create obstacles for issuers and investors. As the market continues to evolve, it is essential to establish clear regulations that encourage transparency and facilitate the growth of green bonds.
4. Competition from Other Sustainable Investments
As the landscape of sustainable finance diversifies, green bonds face competition from other investment products, such as impact funds and ESG-related equities. Investors may need to assess their preferences and consider how green bonds fit within their broader investment strategies.
The Future of Green Bonds
1. Continued Market Growth
Given the increasing focus on sustainability and climate action, the green bond market is expected to continue its upward trajectory. As more issuers recognize the benefits of green financing, new opportunities are likely to emerge.
2. Evolving Investment Strategies
Investors will increasingly look for opportunities to integrate sustainability into their investment strategies. This shift will likely lead to the development of new financial products that cater to the growing demand for environmental responsibility.
3. Enhanced Impact Measurement
As the market matures, stakeholders will demand clearer methodologies for measuring the environmental impact of funded projects. Enhanced impact measurement frameworks will help build trust and transparency, further encouraging investment in green bonds.
4. Greater Collaboration
Collaboration among stakeholders, including governments, financial institutions, and non-profits, will be essential for advancing the green bond market. Collaborative initiatives can facilitate knowledge sharing, promote investor education, and bolster the credibility of green bonds.
Conclusion
The rise of green bonds in financial markets represents a significant shift towards sustainable financing solutions. As environmental concerns become more pressing, green bonds offer investors a unique opportunity to support projects that promote sustainability while achieving financial returns.
While challenges remain, the continued growth of the green bond market signals a collective commitment to addressing climate change and fostering a more sustainable future. By investing in green bonds, individuals and institutions can contribute to meaningful environmental initiatives and drive positive change.
As we look ahead, the green bond market is poised for further expansion, emerging as a vital component of the global financial landscape. Engaging with this evolving market can empower investors to align their financial goals with their values, fostering a sustainable economy for generations to come.
Related
-
Financial News

-
Cryptocurrency

-

-
Forex Market

-
Economic Indicators

-
Forex Market